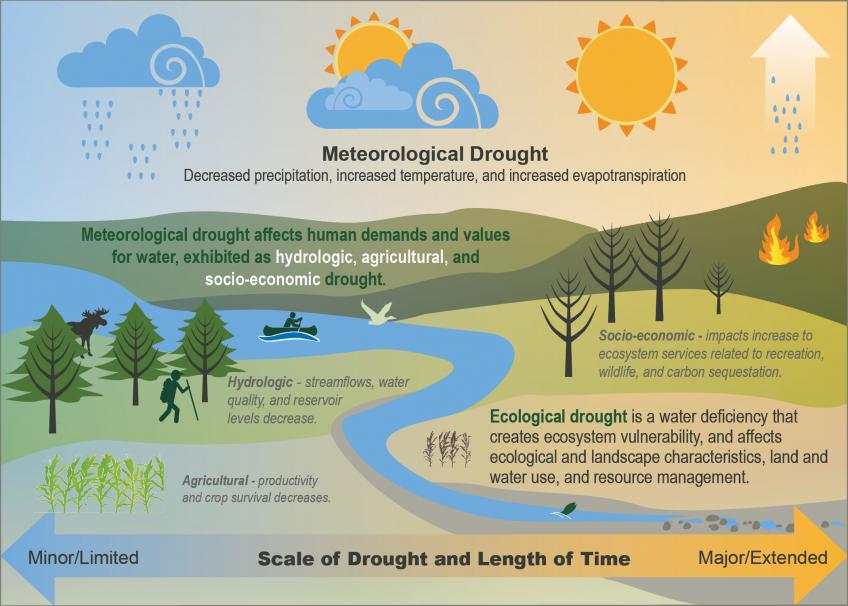
Drought
Meteorological drought refers simply to an increase in dry weather conditions, from reduced precipitation and increased temperatures. This can lead to:
- Hydrological drought: Reduced water in streams, lakes, and reservoirs.
- Agricultural drought: Reduced crop survival and productivity.
- Socio-economic drought: Reduced supply of economic goods (such as food and timber), such that these are unable to meet demands.
- Ecological drought: Ecosystem effects of drought, which can increase ecosystem vulnerability to other disturbances, and can affect a variety of plants and animals in forests and rangelands.
All of these can have major consequences. Reduced water quantity and quality can result in shortages to clean drinking water in communities, as well as reduced water supply for agriculture, ranching, and other human needs. It can harm fish and wildlife, and reduce opportunities for recreation such as boating and fishing. Drought can kill plants directly, leading to changes in forest composition and structure, as well as nutrient, carbon, and water cycles. It can also contribute to wildfires, insect and disease damage, the spread of invasive species, and other disturbances, all of which in turn affect natural areas and local communities.
Droughts have been increasing in recent years in much of the country, a trend that is expected to continue. Although precipitation patterns are complex, increased temperatures alone can lead to more droughts, and severe droughts are projected to increase in frequency in most regions of the United States.
In order to better understand the consequences of drought, the Forest Service prepared a report, Effects of Drought on Forests and Rangelands in the United States: A Comprehensive Science Synthesis.
Management Options
Although droughts cannot be prevented, smart planning and management action can reduce their impacts, speed recovery, and make forests and rangelands more resilient to future droughts.
Forest managers can reduce water demand by:
- Planting trees that require less water and that have greater drought tolerance.
- Managing stands at lower densities.
- Restoring streams and wetlands to provide better fish and wildlife habitat under low-flow conditions.
- Reducing water demands by monitoring and managing water use for livestock, agriculture, drinking water, and recreation.
- Improving structural responses to drought by building relationships, sharing information, and collaborating with other scientists and stakeholders; revising best management practices and including drought in planning processes; and establishing long-term drought monitoring programs to better understand how drought is changing on the landscape.
In order to help managers with all of this, the Forest Service published a report, Effects of Drought on Forests and Rangelands in the United States: Translating Science Into Management Responses.
Drought Workshops
In addition to the reports described above, the Forest Service has also led workshops and produced webinars on drought impacts. In 2017, in cooperation with the USDA Climate Hubs, the Forest Service convened regional workshops in each of the nine Forest Service regions, to develop strategies to reduce, mitigate, and recover from droughts. They then prepared fact sheets summarizing the findings of each of these workshops.
The Forest Service also hosted a series of resource-specific webinars on the effects of drought on fisheries, recreation, forest and rangeland ecosystems, and invasive species, and prepared fact sheets summarizing highlights of these webinars.
All of the fact sheets described above are available for download; recordings of webinars are available here.
Additional Resources
The OSC Climate Gallery includes a variety of up-to-date resources on drought and its effects. This includes Story Maps, tools, links, and map viewers on topics such as snow drought, effects of drought on rangelands and forests, the connection between precipitation and wildfire, and more.