About the Forest

Inyo National Forest extends 165 miles near the California and Nevada border. It covers about 2 million acres, mostly on the eastern slope of the Sierra Nevada.
Approximately one million acres are in nine Congressionally-designated Wilderness Areas. Elevations range from 4,000’ in the Owens Valley to 14,494’ at Mt. Whitney, the highest peak in the contiguous United States.
Like all national forests, the Inyo is managed for ecosystem health and multiple uses, as directed by Congress. Although most visitors think of the forest for its recreation, the Inyo National Forest is also used for range, timber, minerals, watershed, and habitat for fish and wildlife.
Recreational opportunities include camping, picnicking, hiking, fishing, equestrian use, and off-highway vehicle use. Ski resorts offer alpine skiing and snowboarding; over 100 miles of trails groomed for multiple purpose winter use (snowmobile, ski, and snowshoe), and approximately 45 miles of trails groomed for cross-country skiing.
Organizational Overview
The Inyo National Forest Supervisor's Office is in Bishop, CA. In this office there are many specialists that cover the whole Forest rather than only one District. Specialists include biologists, soil scientists, hydrologists, engineers and more. Together the Ranger Districts and the Supervisor's Office oversee the entire Inyo National Forest.
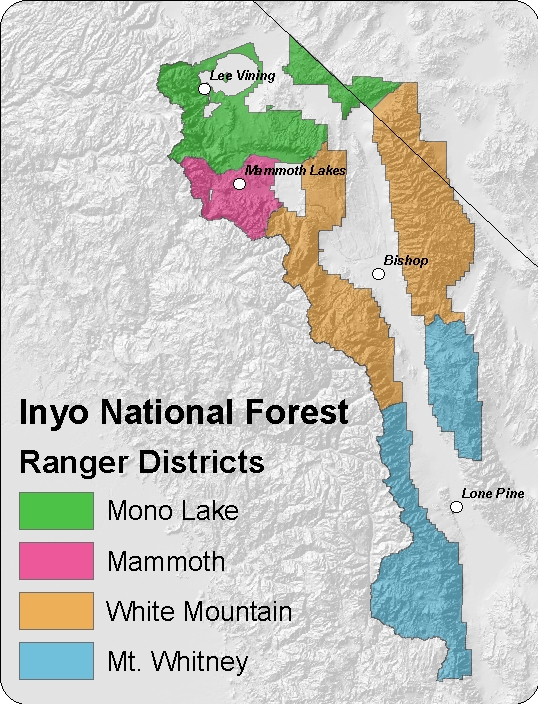
The Inyo National Forest is divided into four Ranger Districts: Mono Lake, Mammoth, White Mountain and Mt. Whitney. Each district has a Ranger Station and/or Visitor Center to meet our visitors' needs.
USDA is an equal opportunity provider, employer, and lender.





